Gold price turns sideways as Fed returns to higher for longer interest rates stance
- Gold price struggles for a direction as the Fed’s “higher for longer” interest-rates stance offsets safe-haven demand.
- Fed Powell supports keeping interest rates at high levels until there is confidence that inflation will ease to 2%.
- The US warns about sanctions on Iran in response to their attack on Israel.
Gold price (XAU/USD) balances below $2,400 in Wednesday’s European session. The precious metal struggles to recapture new all-time highs around $2,430 as Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell emphasised maintaining the restrictive policy framework for a longer period. Powell and his colleagues seem to be leaning towards keeping interest rates higher for longer as inflation has remained stubborn and the labor demand remained strong.
The prospects for the Fed keeping interest rates higher for longer bodes well for the US Dollar and US bond yields. 10-year US Treasury yields fell slightly but remained close to a five-month high around 4.70%. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which measures the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, turns sideways after refreshing a five-month high near 106.40.
Meanwhile, deepening Middle East tensions hold strong ground for Gold. Israel prepares to respond to Iran’s attack. However, US President Joe Biden said it won’t support the counterattack from Israel. US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen said on Tuesday that the US administration intends to levy new sanctions on Iran after it attacks Israel. Fresh sanctions on Iran could impact their capacity to export Oil.
Daily digest market movers: Gold price consolidates inside Tuesday’s range
- Gold price trades below the crucial resistance of $2,400. The precious metal consolidates as a hawkish interest rate outlook from Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell has limited the upside while escalating Middle East tensions continue to offer firm ground.
- On Tuesday, Jerome Powell supported keeping interest rates higher for a longer period as current inflation data is not giving confidence that price pressures will return to the desired rate of 2%. “The recent data have clearly not given us greater confidence, and instead indicate that it’s likely to take longer than expected to achieve that confidence,” Powell said, according to Reuters.
- Powell added that strong labor demand and slowing disinflation progress in the first three months of this year suggest that the restrictive monetary policy framework should be given more time to work to bring inflation down to 2%.
- The Fed’s confidence in progress in inflation easing to the required rate of 2% was questioned after the March Consumer Price Index (CPI) data surprisingly rose more than estimated. Also, robust Retail Sales data for March have reinforced expectations that the inflation outlook will remain stubborn.
- On the geopolitical front, escalating Middle East tensions keep the safe-haven bid firm. Fears of Middle East tensions spreading beyond Gaza have escalated as Israel prepares to retaliate for the airstrike by Iran on their territory on Saturday. Iran aimed hundreds of drones and missiles at Israel in response to their attack on the Iranian embassy near Damascus in Syria, in which two high-ranked generals were killed. The appeal for Gold as a safe-haven asset strengthens when investors see geopolitical tensions worsening further.
- Meanwhile, Fed policymakers are lined up to provide fresh guidance on interest rates this week. Policymakers are expected to maintain the argument that interest rates need to remain higher for long enough until they get evidence that inflation will sustainably return to the desired rate of 2%.
Technical Analysis: Gold price remains below $2,400
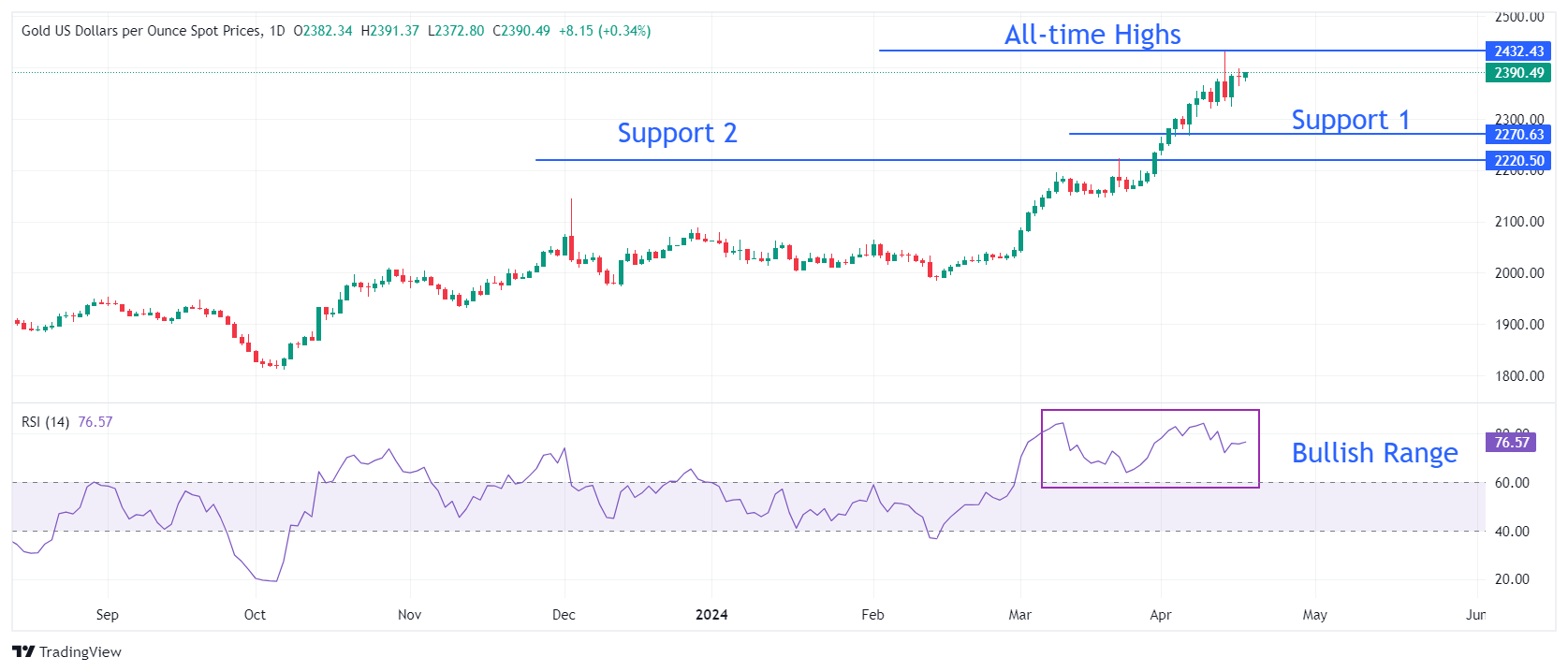
Gold price trades sideways inside Tuesday’s trading range around $2,380. The upside in the precious metal remains limited as momentum oscillators are cooling down after turning extremely overbought. The 14-period Relative Strength Index (RSI) on the daily chart drops slightly after peaking around 85.00. however, the broader-term demand is intact as the RSI remains in the bullish range of 60.00-80.00.
On the downside, April 5 low near $2,268 and March 21 high at $2,223 will be major support areas.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.